Detect respiratory compromise early — there’s no time to waste.
Continuously monitor your patients — safely and simply.
Respiratory compromise is costly and deadly1
Especially in procedural sedation and patient recovery
areas like medical-surgical units.
Respiratory compromise is a
decline in respiratory function
that if left unaddressed will
likely lead to respiratory
failure or death.2
Failure to detect and
prevent respiratory
compromise is associated
with significant human
and economic toll.1
Focusing on detection
and subsequent prevention
is key to reducing the
impact of respiratory
compromise.1-3
39.4%
In-hospital mortality rate
of patients with acute respiratory compromise4
$26,571
Excess hospitalization costs associated with respiratory compromise5
15 days
Respiratory compromise associated excess hospital days6
Safety made simple
To keep patients safe in procedural sedation and medical-surgical units, you need every advantage you can get.
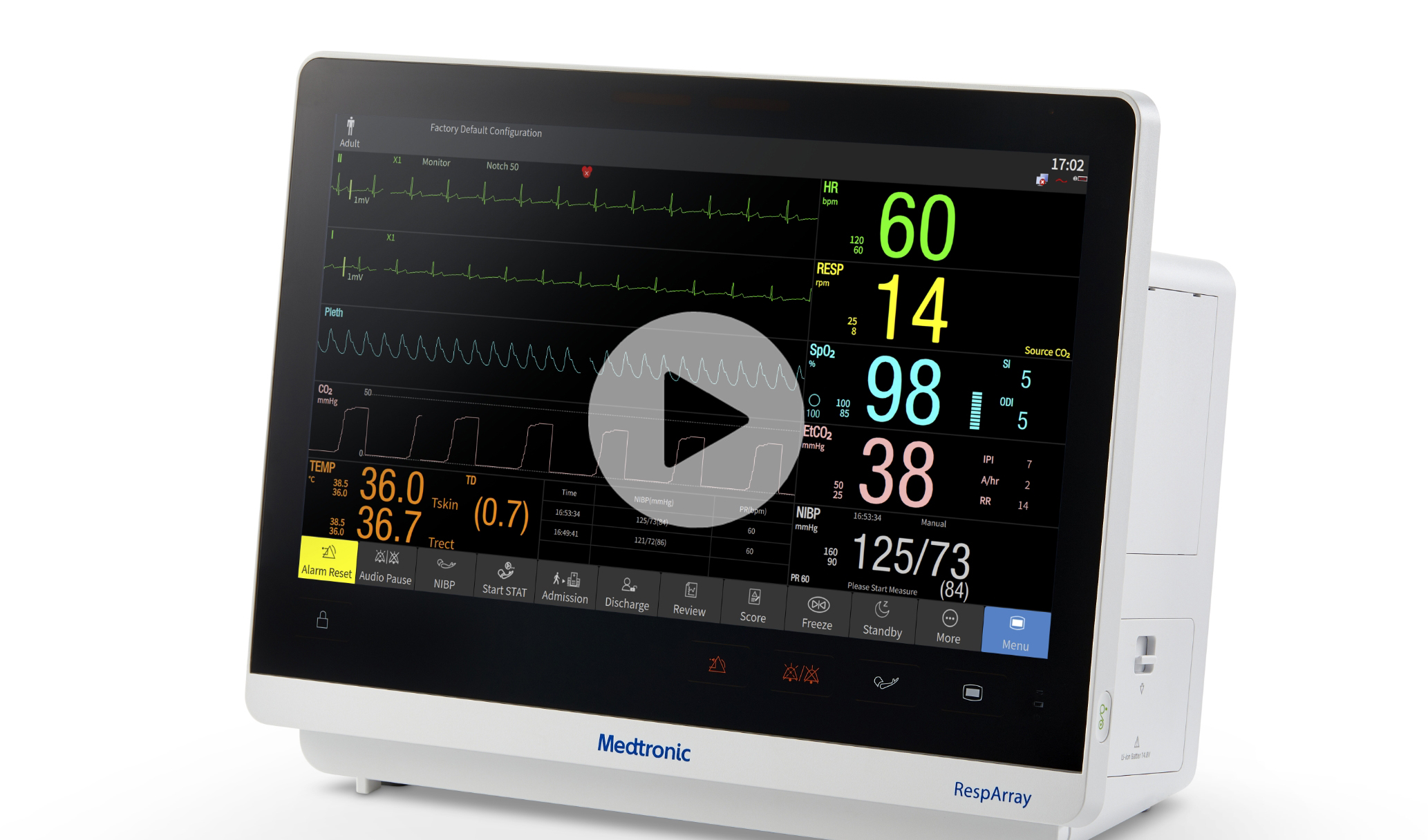
Meet the RespArray™ patient monitor:
- Designed for procedural sedation and medical-surgical units
- Designed to help clinicians detect respiratory compromise in its early stage with built-in Nellcor™ pulse oximetry and Microstream™ capnography technology
- Monitors ECG, NiBP, and continuous temperature monitoring
- Wirelessly connects to EMR and compatible remote monitoring platform
- Easily integrates into your workflow
Contact a representative
For more information on the RespArray™ patient monitor,
contact a Medtronic team member today.
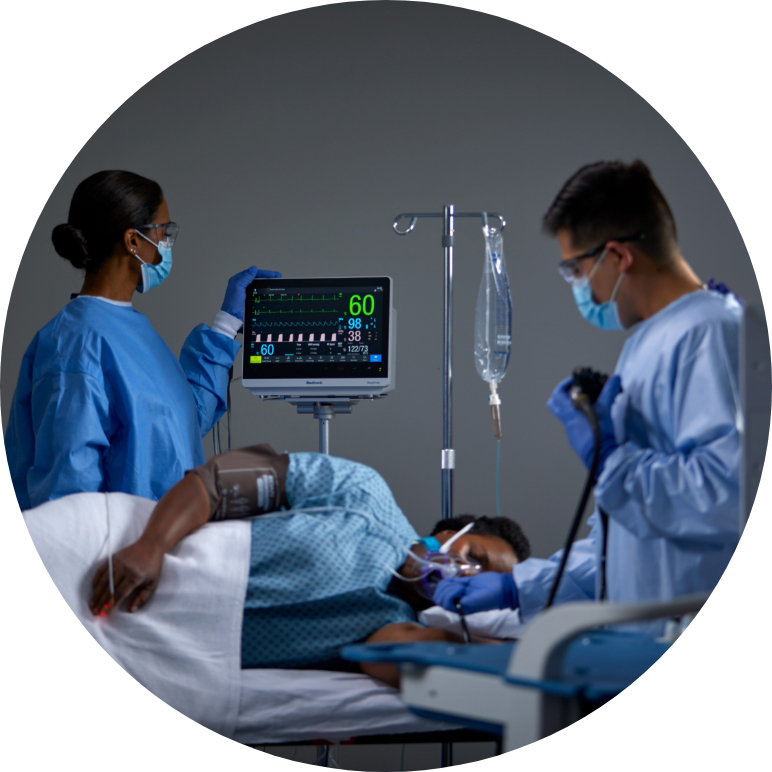
The most common adverse events during procedural sedation are apnea, hypoxemia, and aspiration, which are all the result of respiratory compromise. Capnography monitoring, in addition to SpO2 monitoring, can provide clinicians with a more rapid indication of respiratory decline, and help you detect 23X more episodes of respiratory compromise, compared to using SpO2 alone.7
With the RespArray patient monitor, you can:
- Manage patient risks with continuous monitoring and safety
- Get data quickly to detect respiratory compromise early
- Experience world-class Nellcor™ pulse oximetry and Microstream™ capnography technologies designed to help clinicians detect respiratory compromise early — and help reduce alarm fatigue
- See trends with near real-time monitoring so you can get to your patients sooner
Go beyond spot-checking in the medical-surgical units
It's important to get a complete picture of your patient's respiratory status, so you have the coincidence your patient is safely sedated and receiving effective pain management, especially knowing that:
- Spot checking may be inaccurate
- Intermittent pulse oximetry spot checks missed 90% of hypoxemic episodes8
- Acute respiratory compromise on inpatient wards has an associated in-hospital mortality of approximately 40%4
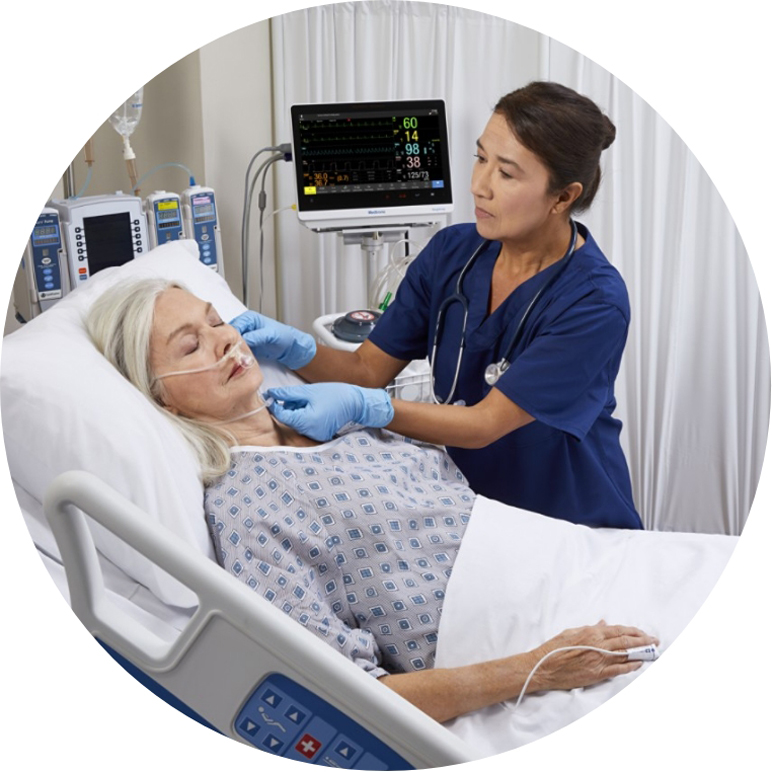

Improve detection ability and workflow in medical-surgical units
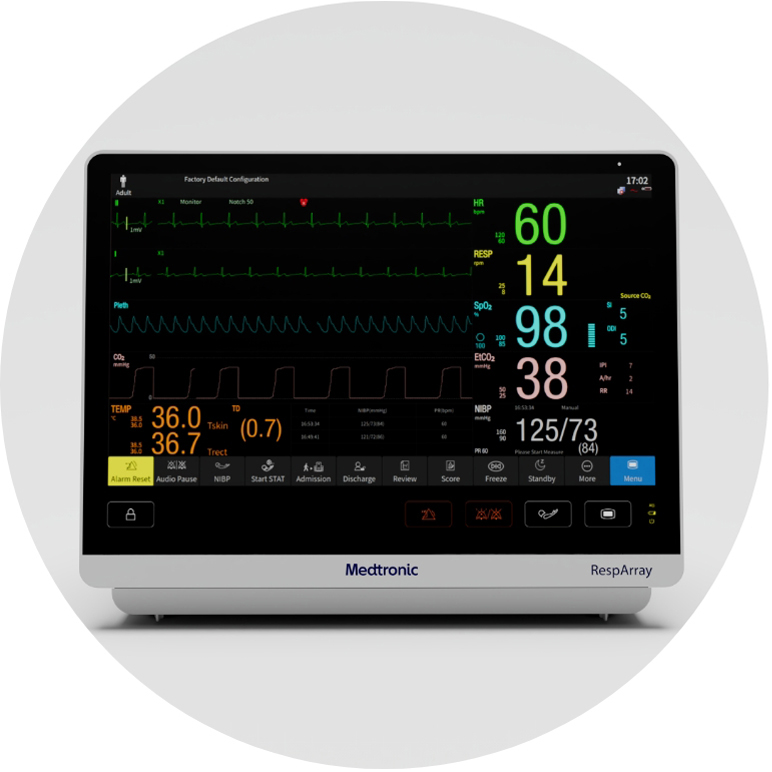
Continuous monitoring could improve safety and reduce workload for clinicians.10
The RespArrayTM patient monitor:
- Features connectivity and seamlessly integrates into workflow, so you'll have have more time to focus on your patients.
- Includes an HL7 interface, is WiFi-enabled, and connects to your EMR and Vital Sync™ remote surveillance — giving you more visibility, wherever you are.
- Features a large, intuitive touch screen you can see from multiple angles and from a distance.
PRODIGY: Risk prediction tool for respiratory depression
Learn more about the easy-to-use PRODIGY Risk Prediction Tool that helps healthcare providers identify which patients in medical-surgical units would benefit most from continuous monitoring.11
"Continuous monitoring technologies should not be used as the sole basis for diagnosis or therapy and are intended only as adjuncts to patient assessment"
References
1. Lee LA, Caplan RA, Stephens LS, et al. Postoperative opioid-induced respiratory depression: a closed claims analysis. Anesthesiology. 2015;122(3):659-665.
2. Morris TA, Gay PC, MacIntyre NR, et al. Respiratory Compromise as a New Paradigm for the Care of Vulnerable Hospitalized Patients. Respiratory care. 2017;62(4):497-512.
3. Quach JL, Downey AW, Haase M, Haase-Fielitz A, Jones D, Bellomo R. Characteristics and outcomes of patients receiving a medical emergency team review for respiratory distress or hypotension.
Journal of critical care. 2008;23(3):325-331.
4. Andersen LW, Berg KM, Chase M, Cocchi MN, Massaro J, Donnino MW. Acute respiratory compromise on inpatient wards in the United States: Incidence, outcomes, and factors associated with in-hospital
mortality. Resuscitation. 2016;105:123-129.
5. Melamed R, Boland LL, Normington JP, et al. Postoperative respiratory failure necessitating transfer to the intensive care unit in orthopedic surgery patients: risk factors, costs, and outcomes. Perioperative
medicine (London, England). 2016;5:19.
6. Fischer JP, Shang EK, Butler CE, et al. Validated model for predicting postoperative respiratory failure: analysis of 1706 abdominal wall reconstructions. Plastic and reconstructive surgery. 2013;132(5):826e-835e
7. McCarter T, Shaik Z, Scarfo K, Thompson LJ. Capnography monitoring enhances safety of postoperative patient-controlled analgesia. Am Health Drug Benets. 2008;1(5):28-35.
8. Sun Z, Sessler DI, Dalton JE, et al. Postoperative hypoxemia is common and persistent: a prospective blinded observational study. Anesth Analg. 2015;121(3):709–715.
9. Semler MW, Stover DG, Copland AP, et al. Flash mob research: a single-day, multicenter, resident-directed study of respiratory rate. Chest. 2013;143(6):1740-1744. doi: 10.1378/chest.12–1837.
10. JAMA; February 25, 2022
11. Medtronic. Prediction of opioid-induced respiratory depression in patients monitored by capnography (PRODIGY). Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02811302. ClinicalTrials.gov Identier:
NCT02811302.